What is an Allergy

Allergy is a condition, often inherited, in which the immune system of the affected person reacts to something that is either eaten, touched, or inhaled that doesn’t affect most other people. The patient’s immune system reacts to this substance as if it were an “enemy invader” (like a virus). This reaction leads to symptoms that often adversely affect the patient’s work, play, rest, and overall quality of life.
Allergens Cause Allergies
Any substance that triggers an allergic reaction is called an allergen. Allergens “invade” the body by being inhaled, swallowed or injected, or they may be absorbed through the skin. Common allergens include pollen, dust and mold.

What are the Symptoms of Ear, Nose and Throat Allergies?
- Repeated sneezing
- Nasal itching and rubbing
- Nasal congestion
- Runny nose
- Dark circles under the eyes
- Crease across bridge of nose
- Frequent throat clearing
- Mouth breathing
- Diminished/lost sense of smell/taste
- Recurrent, unexplained nosebleeds
- Recurrent ear infections
- Recurrent sinus infections
- Fluctuating hearing loss
- Cold-like symptoms more than 10 days Symptoms recur same time each year
- Chronic fatigue
- Symptoms can range from minor to severe
The greater the frequency and/or amount of exposure, the greater the chance that the susceptible person will develop an allergic problem that will require treatment.
What causes Symptoms to Begin?
How do we make the Diagnosis?
The initial or presumptive diagnosis of allergy is made by history and physical examination. If one wishes to be certain of the diagnosis and proceed to treat the patient effectively, the findings must be confirmed by tests that identify the specific offending allergens.
Throat Services
Throat problems can disrupt sleep, breathing, and general good health. Fortunately, treatments can be fairly routine and effective for these patients. We deal with tonsillitis, adenoiditis, adenoid hypertrophy as well as many conditions related to voice, swallowing, hoarseness and infections.
Tonsils and adenoids are the body’s first line of defense as part of the immune system. They sample bacteria and viruses that enter the body through the mouth or nose, but they sometimes become infected. At times, they become more of a liability than an asset and may even cause airway obstruction or repeated bacterial infections.
What are Tonsils and Adenoids?
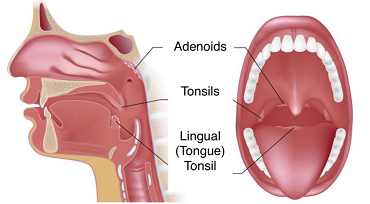
Tonsils are the two round lumps in the back of the throat. Adenoids are high in the throat behind the nose and the roof of the mouth (soft palate) and are not visible through the mouth or nose without special instruments.
What Affects Tonsils and Adenoids?
Tonsillitis and Its Symptoms
Enlarged Tonsils and/or Adenoids and Their Symptoms
- Breathing through the mouth instead of the nose most of the time
- Nose sounds blocked when the person speaks
- Chronic runny nose
- Noisy breathing during the day
- Recurrent ear infections
- Snoring at night
- Restlessness during sleep, pauses in breathing for a few seconds at night(may indicate sleep apnea).
Treatment
In adults, the possibility of cancer or a tumor may be another reason for removing the tonsils and adenoids. In some patients, especially those with infectious mononucleosis, severe enlargement may obstruct the airway. Need more education, call us now
Dizziness

Dizziness is a non-specific term that can represent a host of different symptoms. While it generally refers to an abnormal sensation of motion, it can also mean imbalance, lightheadedness, blacking out, staggering, disorientation, weakness, just to name a few. Symptoms can range from mild brief spells to severe spinning lasting hours accompanied by nausea and vomiting. For clarity of discussion, the common types of dizziness are defined below.
A general term that refers to an abnormal sense of balance and equilibrium.
Inability to keep one’s balance especially when on the feet, e.g. standing or walking.
A near pass-out or faint-like sensation, similar to the feeling if one breath-holds for a prolonged period.
Vertigo is defined as a sensation of movement and does not always involve a perception of spinning. In some patients the symptoms may be subtle and involve only a sensation of “swaying” or of an “inability to focus”. Some patients will experience movement of their surroundings or may feel like the ground is unstable. Sensations of vertigo typically are produced by an abnormality of the inner. Maintenance of balance requires that multiple organ systems in the body execute perfect coordination.
The brain is the central processing center that manages incoming balance information from the various Sense organs and outgoing information directed to the muscles and skeleton. Sensory input comes from three main areas: vision, inner ear, and touch (from the feet and joints). Vision is an important cue to the brain and allows us to determine if we are moving relative to our surroundings.
Diagnosing the Problem
- How often are you “dizzy” and how long does it last (seconds, minutes, hours, days)
- Do you have spells or are your symptoms constant
- Have you had blood pressure of heart problems in the past
- Do you have hearing loss, ringing or fullness of the ears, headache, severe allergies
- Do you get worse with changes in position, weather changes, mental stress, exertion
- Do you have difficulty maintaining your balance in the dark or on soft surfaces
- Do you have short term memory loss or a lack of concentration
- Have you had panic attacks or depression
- Is there a family history of vertigo, imbalance, tremor, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, etc.
- Do you have a history of stroke, migraines, TIAs, seizures
- Have you fallen or nearly fallen recently
- Have you had any recent vaccinations
- Do you have a history of problems with insulin metabolism (Diabetes, hypoglycemia)
Ear Infections
Earache is common but does not always occur. Dulled hearing may develop for a few days. High temperature (fever) is common. Children may feel sick or vomit and can be generally unwell. Young babies cannot point to their pain. One of the causes of a hot, irritable, crying baby is an ear infection. Sometimes the eardrum bursts (perforates). This lets out infected mucus and the ear becomes runny for a few days. As the pain of earache is due to a tense eardrum, a burst eardrum often relieves the pain. A perforated eardrum usually heals within a few weeks after the infection clears.
Sinus Services
Sinus infection occurs in two types. Acute sinusitis gives rise to severe symptoms but is usually short-lived. Acute sinusitis usually occurs following a cold. Typically a green-yellow nasal discharge occurs a week or more after the onset of the cold and this is associated with severe pain around the cheeks, eyes and/or forehead. This may be associated with swelling and a high fever along with toothache. Chronic sinusitis is sinusitis that continues for many weeks. Chronic sinusitis may be caused by an acute sinus infection which fails to resolve or as a result of an underlying allergy affecting the lining membranes of the nose and sinuses. Common symptoms include nasal obstruction, headache, nasal discharge, low grade fever, reduced sense of smell, facial pain and halitosis.
Acute sinusitis is usually treated with antibiotics and medication to reduce the swelling of the nasal lining e.g. decongestants. Chronic sinusitis may need long term treatment. Medical treatment options include antibiotics, decongestants and other treatments to reduce the swelling of the lining such as nasal steroid sprays. Antihistamines will have a place in patients who have an underlying allergy. In the vast majority of cases sinusitis can be managed effectively with medical treatment. Occasionally symptoms will persist despite ongoing use of medicines in which case surgery may be necessary. The diagnosis of sinusitis by a specialist will involve the use of a nasal endoscope which the doctor can use to examine the nasal lining and the sinus openings.